Google Security - Page 1
Google cloud Professional Security Engineer
The exam itself, is a multiple choice 2 hour test.
Regions and Zones
When we architect our application we need to deploy our application closes to our users, as well as spanning multiple zones.
Google cloud is split into Regions and Zones
- Region
- A geographical location that the DC sits in
- Example being europe-west2
- Zone
- A specific Data Centre in the Region
- Example being: europe-west2-c
Some applications (Like the ones I am working on currently) - We are not allowed to store Date outside the border of the United Kingdom.
Whilst Google don't release information about their exact locations, we are able to make a good guess it's in Slough
These data centers are connected via High speed connections (Fibre cables)
GCP Services
- Encryption
- Allows Google Managed keys
- Allows uploading your own keys
- VPC
- Secure private cloud
- VPC Peering
- Peers VPC's between projects and accounts
- Routes traffic
- VPC Sharing
- Allows projects to put resources on a shared VPC
- Hybrid Connectivity
- Secure private connection between your premise and the cloud
- Data Loss
- Detect sensitive Data and scrub it
- Security Command Centre
- Allows us to view all security issues
- Binary Authorization
- Allows only certain docker images to run
- Web Security Scanner
- Scans internal web apps for security vulnerabilities
- IAM & Admin
- IAM
- Identity and Access Management
- Who can do what, when and with what
- IAM
Security at Google and how it helps
- What google does to secure your app/ data
- How google does all these
- Security Mechanisms at different layers
- Shared Responsibility model
- Tools provided by GCP
- Regulatory Compliance
Why trust google
- They have over 7 billion users
- Security is a main concern for them
- Your applicaiton is deployed in the same infrastructure as Google.com and google workspaces applications
- They have dedicated engineers 24/7 working for security
How google Secure their infrastructure
- Hardware layer
- Less than 1% of Google employees have access to the Data Centre
- Google builds all their own hardware
- Routers, switches, etc
- IAM
- Identity and access management
- Allows users to do some stuff and blocks them to do others
- User Management
- Google Account authentication
- SMAL support
- Enforce user rules
- 2fa
- Minimum password
- Google Account authentication
- Storage data
- Encrypts all your data
- Keys:
- Google managed by default
- Customer Supplied
- Customer Managed
- IAP
- Identity Aware Proxy
- Secures Applications via google login
- Built in DDOS prevention
- DLP
- Inspects Data
- Can be configured to Find and Redact
- Transform data
- Can be used to re-identify it
- VPC
- Firewall rules
- Cloud Armour
- Ingress/ Egress rules
- Operations
- Logging
- Monitoring
- Tracing
- Profiling
- Regulatory Compliance
- Encryption, hardware, VPC firewall is technical aspect of security
- Compliance is another important factor
- Google cloud follows these standards
Shared Responsibility Model
Google is responsible for securing some aspects of your deployment, like the underlying hardware/ infra, whereas you need to ensure that your application is patched (At a bare minimum)
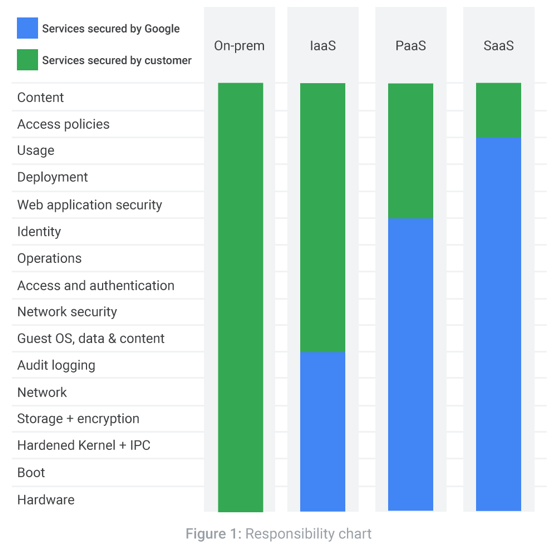
The above chart shows who play more roles around where, and by whom
We can see that for On-prem, it's entirely your problem
Whereas when we go to Software As A Service (SaaS) - All the underlying infrastructure, usage, deployment etc. is the providers' problem.
Cloud Identity
There are 5 'Cloud Identities':
- Google Account
- Service Account
- Google Workspace
- Cloud Identity Domain
- Google Groups
The above are then able to interact with Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
In every single identity, they are similar to Email address'
Cloud Identity is a Managed service that manages users.
Cloud Identity - Google Workspace
This is the renames product previously called G-Suit
- Similar to Office 365
- Slides
- Sheets
- Docs
- Etc
- You can get a verified domain
- Domain like breadnet.co.uk - Verify ownership
- You get complete user management for all the users under the domain
- Free 15 days trial, then $6 per user per month
- Access via admin.google.com
- If you already have Google Workspace, then it automatically verifies your Google cloud domain
Sections have been skipped on Udemy as knowledge is pre-existing
Admin Console
The below section is about the Google cloud admin console
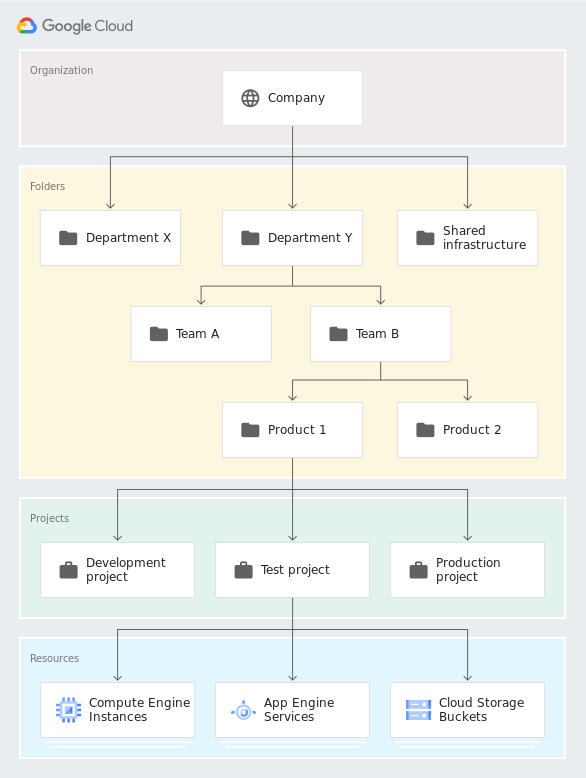
Resource Hierarchy
At the top you have the Organization Below the ORG you can have folders Below folders, you have projects
At each level you are able to set IAM and policies
- You can nest folders up to 10 (ten) levels deep.
- A parent folder cannot contain more than 300 folders. This refers to direct child folders only. Those child folders can, in turn, contain additional folders or projects.
- Folder display names must be unique within the same level of the hierarchy.
Organization Policies
For argument’s sake, we will look at how to enable/ disable 3 policies:
- Disable Service Account Creation
- Enforce Uniform bucket level access
- Skip Default network creation
How to Enable
IAM > Organization Policies > Disable Service account creation
Here we are able to define what level the policy applies at.
How to disable on a project when it's inheriting
If you need to remove something that is inherited, you select Customize > Enforcement > Off
IAM
Intro
- IAM stands for Identity and Access management
- Defines: Who can do what and on which
- Who:
- Identity
- Member
- What
- Roles
- Collections of permissions
- Roles
- Which
- Resources:
- Compute Engine
- app engine
- Bigquery
- etc
- Resources:
- Who:
Roles
There are 3 types of roles in Google Cloud Platform
Roles are defined as a Collection of Permissions
- Primitive
- These are super simple roles, and should usually be avoided as good as possible
- Owner
- Editor
- Viewer
- These are super simple roles, and should usually be avoided as good as possible
- Pre-defined
- These roles are roles on a single service
- Examples:
- Compute admin
- Network Viewer
- BQ Job User
- Examples:
- These roles are roles on a single service
- Custom roles
- These are roles you make for your org or project based on specifics from predefined roles,
- They usually follow the layout like
- service.resource-type.verb
Want to make this site better? Open a PR or help fund hosting costs