Google architect - Page 2
IAM
- Resources
- Humans
- Non-humans
- Identities can be:
- Users
- Groups
- Application running in GCP
- Application running in your Datacenter
- Unauthenticated users
- Granular control
- Limit a singular user
- Perform actions
- On a specific cloud resource
- From a specific IP address
- During a specific time
IAM: Example
- Want to provide access for a colleague to specific cloud bucket
- Important generic concepts
- Member: My Colleague
- Resources: Specific cloud storage bucket
- Action: Upload/ Delete objects
- In google cloud IAM
- Roles: Set of permissions
- Roles do not know about members
- How do you assign permissions to a member:
- Policy: You assign (Or bind) a role to a member
- Choose a role with the right permissions
- Create a Policy binding the members with the role
IAM: Roles
- Roles are permissions
- Perform some set of actions on some set of resources
- 3 types
- basic roles: (or primitive roles)
- Viewers (roles.viewer) read only access
- Editor (roles.editor) Viewer and edit action
- Owner (roles.owner) Editor + manage roles and permissions + Billing
- Not recommended: Don't use in prod
- Predefined rules - fine-grained riles predefined and managed by google
- Custom roles - when pre-defined roles are not sufficient
- If creating a role, ensure you give it a good ID
- There are also role versions to use, so:
- Alpha, beta, General availability, Disabled
- Most of the roles will give you:
- resourcemanager.projects.get
- resourcemanager.projects.list
IAM - Most important concepts
- You create a role which contains the permissions
- You bind the role to a user with a policy
IAM - Service accounts
- An application needs to auth with something on the GCP platform
- You do not want to use an actual account for this, so you use a service account
- Identifiable via email:
- Does not have a password
- Has a private/public rsa key
- cant login via browser or cookies
- Service account types
- Default service account - Not recommended to use
- User managed - User created
- Provides fine-grained access control
- Add roles to the service account if you're backing up to GCS
- You cannot assign a service account to an on-prem application
-
This is called long-lived
-
Create service account with right permissions
- Create service account user managed keu
- gcloud iam service-accounts keys create
- Make the service account key accessable by your application
- ENV variable should be: GOOGLE_APPLICATION_CREDENTIALS
-
use google cloud client libraries - ADC (Application default credentials)
-
Short-lived:
- Few hours of access
- Credential types:
- Oauth2
- OpenID Connect ID tokens
- Service to service authentication for short periods of time
- Self signed json web tokens
IAM Best Practices
- Principle of least privelage
- Give the least possible privelage needed for a role
- Use service accoutns with Minimum privelages
- Seperation of Duties
- Involve at least 2 people
- Have seperate traffic deployer and traffic migrator roles
- Breaks up issues from one person not seeing something
- Constant monitoring
- Always view the logs and see who is accessing your service account
- Ensure audit logs are archived
- Use groups when ever possible
- Bind roles to groups
- Just add a new user to the group
Understanding Identity managment
- Email used = Super Admin
- Google Workspace
- If you use workspace, you can link them and manage groups from there
- Not using Workspace
- You can link your identity provider
- Federate google cloud with your identity provier
- Fererate
- You want to auth with your external idP (Identity provider)
- Example isActive directory
- We can 'Federate' cloud identity
- Example:
- Federate AD with GCDS then ADFS
Corporate directory federation
- Federate identity provider with your external IDP
- Enable SSO
- Users go to google cloud
- Redirected to external IDP
- Users sign in
- SAML assertion is sent to GCP
Iam Members/ Identities
- Google account
- Service account
- Google group
- Unique email adress
- Manage permissions in one place
- Workspace Domain
- Cloud Identity as a service (IDaaS)
ACL - Access control list
- Access Control Lists define who has access to your buckets and objects
- How is this different from IAM?
- IAM permissions apply to all objects in a bucket
- ACL's can be used to customize specific access to different objects
- Users get access if they are allowed by either IAM or ACL
- Use IAM for permissions to the whole bucket (Uniform access)
- ACL for access to individual objects
- Buckets have 2 levels:
- Fine-grained
- Per object access
- Uniform
- NO object level ACL
Signed URL
- Allow users to access the objects for a short period of time
- No login required
- Create a signed URL with a service account with the desired permissions, then create a key for that URL, and assign it to the signed URL
gsutil signurl -d <number>m <key> gs://<bucket>/<object path>
Web servies
Expose static site using cloud storage
- Create a bucket with the same dns name as your site
- Verify that you own it
- Copy files to the bucket
- Set uniform access to the bucket
- Set to `All Users`
- grant view all objects
Databases
Fundamentals
- Databases provice organized and Persistent storage for your data
- To choose between different databse types we would need to understand:
- Availability
- Durability
- RTO
- RPO
- Consistency
- transactions
Availability and Durability
-
Availability
-
Will I be able to access my data when I need it
-
Percentage of the time an application provides operations
-
Durability
-
Will my data be available in x years
- What does durability mean?
- Not losing data
- How to increase it
- Replicate the data
- Ensure sonsistency
RTO & RPO
- RTO
- Recovery time objective
- Maximum acceptable downtime
- RPO
- Recovery point objective
- Maximum acceptable period of data loss
Read Replicas
If you have an application that has high reads, you can create a read replica
If there is a master failure you can promote one of the slaves to master
Consistency
- Strong consistency
- Synchronized to all replicas
- Transaction will slow down if you have alot of replicas
- Eventual constancy
- A little lag between replication
- Used when scalability is more important than data integrity
- Read after write consisteny
- Inserts are immediately available in all replicas
- Updates are doe via eventual consistency
Categories
- Relational
- OLTP
- Online transaction processing
- OLAP
- Online analytics processing
- Document
- Key value
- Graph
-
In memory
-
Factors
- Do you want a fixed recovery?
- Transaction properties (Atomicity and consistency)
- Latency
- Transactions p/s
- Data stored
Relational Databases
- This was the only option a while back
- Predefined schemas
- Strong transactional capabilities
GCP Databases
- OLTP
- Applications where users make lots of small transactions (updates etc.)
- Popular:
- Mysql
- Oracle
- SQL server
- Recommended managed service:
- CloudSQL
- CloudSpanner
- Unlimited scale and global scale
- OLP
- Running analytics
- Datawarehouse
- BigQuery
Difference between OLTP and OLAP
- OLTP
- Databases use rows
- Each table row is stored together
- Efficient for small transactions
- OLAP
- Each table column in stored together
- High Compression
- Distribute data easily
- Execute query across multiple nodes
NoSql
- New approach
- NoSQL = Not only SQL
- Flexible schema
- Lets the schema evolve with the data
- Horozontal schale to petabytes
- Typical nosql has scability and high performance
- Products
- Cloud Firestore
- Serverless
- Document storage storage
- ACID
- Firestore has SDK's
- Small to medium
- CloudBigtable
- Scalable
- Managed
- recommended for data greater than 10tb to petabytes
- Not reccomended for transactional
- No support for multi-row transactions
- Reccomened for:
- Large streams of data
In memory databases
- In memory stored database
- Retreival is faster
- Service:
- Memory Store
Summary
Database type
GCP Services
Description
Relational OLTP Databases
Cloud SQL, Cloud Spanner
Reansactional use cases needing pre-defined schema and a very strong transactinal capabilities.
CloudSQL : Mysql, postgres sql
CloudSpanner: Unlimited scale and 99.999% availability
Relational OLAP Databases
BigQuery
Column storage with pre-defined schema. Datawarehouse and big data
NoSQL
Cloud firestore, Cloud Bigtable
Apps needing quick evolving structure (Schema-less)
Cloud firestore: Serverless transactional document DB, 0.5tb
BigTable: Large database (10tb+) straming IOT and analytical workloads. Not serverless
In memory databases/ cache
Cloud Memory store
Applications needing microsecond response
CloudSQL
- fully managed Database
- Supports MySQL, PostgreSQL and SQL Server
- Regional Service
- SSD or HDD
- up to 416 RAM and 30TB
- Use cloud SQL for Simple relational Cases
- Migrate Local MySQL
- Reduce maintenance costs
- Use cloud Spanner instead of CloudSQL IF:
- Huge amounts of data
- Need infinite scaling
- Global distribution
- Higher availability
To connect
gcloud sql connect <instance name> --user=root --quiet
Features
- Automatic encryption (Tables and backup)
- Highavaliblity and failover
- Create a standby with automatic failover
- Pre-req: Automated backups and binary logging
- Read replicas
- Cross zone, cross region
- Automatic storage increase
- Point in time recovery
- Pre-req: Enable binary loggong
Best practices
- Cloud SQL PROXY
- securly connect to the cloud SQL from your apps
- Understand Scalability
- Enable HA configuration for HA
- Read replicas help you offload read workloads
- Does not increase avalability
- Have a number of cloudSQL instances opposed to one large one
- Cant distribute the writes
- Backup
- Backups are lightweight and provide point in time recovery
- Cannot copy or do operations on the backups
- Cannot backup a single database or table
- have to back up the entire database
- Export
- Takes longer but more flexibility
- Export single database or table
- Exporting large database impacts the performance
Cloud Spaner
- Fully managed, Mission Critica relational sql and globally distributed
- Strong transactinal
- Scales to PB
- Scales horozontially
- pay per node and per storage
- Data export: Cloud console
- Data flow
- No glcoud
No SQL
Cloud Datastore and Firestore
- Datastore
- Highly scalable NoSQL Document Database
- Recommended for up to a few TB
- Structure: Kind > Entity
- flexible schema with transactions
- Export only from gcloud
- Export contains metadata file
- Being replaced with Firestore
- Firestore
- Offline mode and data synch
- Provides libraries
- Offers datastore in native moce
- Both Serverless
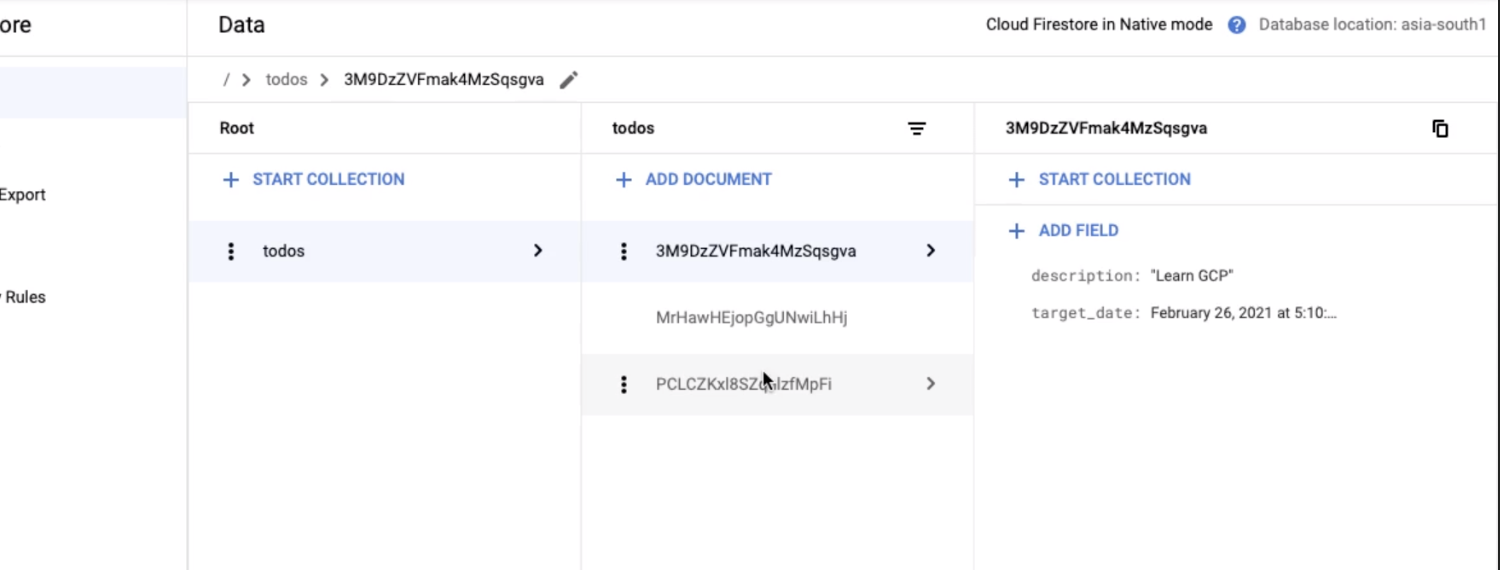
Storing data in Firestore
- Collection
- One or more document
- Sort of like a table
- Document
- Has an ID
- Has fields and values
-
Indexes
- Automatically created
- Provides a simple ability to search
- Ability to pick where you query
- Cloud firestore automatically indexes fields you add
- Exporting
- Entire database
- Collections
- Location:
- GCS
Cloud Datastore
- Datastore is a document store with flexible schema
- Recommended for storing things like user profiles
- Use case: Index for objects stored in cloud storage
- You want to allow users to upload profile pictures
- Enable quick searching by storing metadata
- Design your keys and indexes carefully
- Avoid monotonically increasing values as keys
- Numbers, customer1... or timestamps
- Create only indexes that will be created in searches
- For adhoc, you'll want to use bigquery
- Prefer batch operations
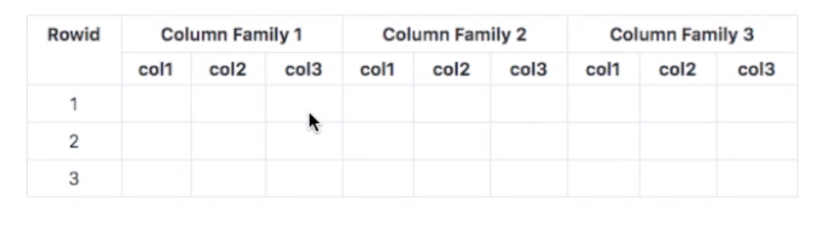
Cloud BigTable
- Petabyte scale, wide column
- NoSQL (HBase API Compatible)
- Designed for huge volumes of Analytical and Operational data
- Handles millions of reads and writes
- Single row transactions
- NOT Serverless
- Cannot export using console or gcloud
- Either use the .jar or
- HBase
- Command line
- cbt
Wide Column
- Each table is a sorted key/ value map
- Each row is indexed using a row key
- Structure supports high read and write low throughtput latency
- Use cases:
- IOT Streams, graph data, real time analytics
- Transactional stock
Designing BigTable tables
- What data do you want to store
- What would your frequent used queries look like?
- Design your key/value store
- Each table only has one index
- You can store multiple key segments, separated by a deliminator
- If you frequently search recent data
- Start backwards so most recent data is first
Best practices
- Recommended for streaming IOT and Time Series
- Automatically shards data in to multiple tablets
- Tablets are distributed accross different nodes
- Goals:
- Same amount of data on each node
- Distribute reads and writes equally
- Pre-test with heavy load
- This is for allowing the nodes to balance themselves
- Supports HDD and SSD
- SSD for latency sensitive
- Increase reliability and durability
- Create multiple replicated clusters
- Can create a cloud bigtable cluster with many clusters accross regions
- As well as cross zone
- Stored data indiepndantly
- Store the data closer to the users
- Configure an app policy with routing
Networking
VPC
- VPC
- Can contain many subnets
- Regional
- Subnets
- To close off things from public you use a subnet
- You have 2 subnets
- Private
- Nothing here can be access from the internet
- Public
- Creating a VPC
- Option 1: Auto Mode
- Subnets are created in each region
- Default VPC created automatically
- Option 2: Custom mode VPC
- No subnets are created
- You have complete control over subnets and their IP ranges
- Prod recommendation
- Options when creating a subnet
- Enables private IP access for communication with Google network
- Enable Flow logs to see inbound and outbound network traffic
Creating the VPC
- Creating the VPC
- Required values
- Name
- Region
- subnet
- Private google access
- Should vm's in the subnet be able to access google resources with no public IP
Shared VPC
- Shared VPC
- Allowing shared VPC's to connect to multiple service projects
- Host project: Contains shared VPC Network
- Service projects: Attaches to host projects
VPC Peering
- VPC Peering
- You can peer multipe VPC's together
- All communication happens inside Google's network
- Network Administration isn't changed
Firewall rules
- Firewall rules
- Allow access in and out
- Stateful rules
- If in is allowed then out is allowed
-
Each firewall rule has a priority
- 0: Highest
- 65535: Lowest
-
Default rule
* Egress allowed * Deny Ingress- Default VPC
- the default VPC has 4 default rules with the priority 65534
- Called fefault-allow-internal
- Ingress rules:
- Target: Defines the destination
- Targeting it: Service account or tag
- Source:
- Defines where the traffic is coming from
- Targeting it: Tags or Service accont
- Each rule:
- Priority
- Action on match
- Allow or deny
- Protocal
- Enforcment status
- Enable or Disable
Best practices
- Cloud load balancing instances:
130.211.0.0/2235.191.0.0/16- Remove 0.0.0.0/0 from source IP
Cloud Operations
Operations
- Cloud Operations
- To operate cloud effectivly yous hould know
- Is my application healthy
- Does my DB have enough space
- Are my servers healthy
- Cloud monitoring
- Measurments
- Graphing
- Alerts
- Channel
- Condition
- Notifications
- Documentation
- Workspace
- In order for it to work you need a 'Workspace'
- It can monitor AWS and GCP
- Creation:
- Create a workspace in a host project
- Add AWS or GCP account
- Default metrics
- CPU
- Dist traffic
- Uptime
- Network traffic
- For more details:
- Add cloud monitoring agent
- works on collectd
Logging
- Real time log managment and alaysis tool
- Allows for storing, searching and analyzin
- Excabyte scale, managed service
- Ingest logs from anywhere
- Key features:
- Log explorer
- Logs dashboard
- Log metrics
- Log router
- Route the logs based on a condition
Collection
- Collection
- Most services already spit logs to GCP logging aggregation service
- Ingest from GCE
- Install logging agent
- Ingest from Onpremise
- Use BindPlane
Audit and security logs
- Audit and securit
- Access transprenct
- Captures actions by the GCP team done on your content
- Only supported for Gold+ levels
- Cloud audit logs
- answers who did what, when and where
- Contains:
- Admin activity
- Data access
- System event audit
- Policy denied audit logs
Feature
Admin Activity logs
Data access Logs
System event logs
Policy denied logs
Logs for
API calls or other actions that modify the configuration of resources
Reading configuration of resources
Google cloud administrative actions
When user or service accounts are denied actions
Default Enabled
Yes
No
Yes
Yes
VM Examples
VM creation, patching, change in IAM
Listing resources
On host maintanace
Security policy violation logs
Cloud storage
Modify bucket or object
Modify/ read bucket or object
Access Needed
Logging/ logs viewer or project/viewer
Logging/private logs viewer or project.owner
logging.logsviewer or project.viewer
logging.logs viewer or project.viewer
Log routing
- Log routing
- Logs from various sources
- Log router checks against configured rules
- Two types of log buckets
- _Required, holds admin activity
- Zero charge
- Cannt change the retention period
- _default
- All other logs
- You are billed based on cloud logging
- you can disable the default log
- Export
- You can export to a bucket
- You can export to a bigquery dataset
- You can export to pub/sub in base64
- You need to create 'sinks'
- This allows you to send logs out to somewhere else
- Sinks and router
- You cant edit the audit bucket and router sink
- You can send logs to other locations
- Big query
- Cloud storage bucket
- Pub/SUb
- Splunk
- Other project
- Alerting
- When something happens you need to create an alet
- Setup alert channels
- then setup policy
- Setup a metric
- Set up the steps to fix
- Uptime checks
- You want to ensure that your applications run all the time
Cloud Trace
- Cloud Trace
- Supports google cloud services
- Instriment applications
- Find out:
- How long does a service take to ahndle
- Average request latency
- Support for
- Multiple languages
Cloud Debugger
- Cloud debugger
- Captures state of running applications
- Inspect the state of the application
- Take snapshots of variables
- No need to add additional logging statements
- No need to redeploy
- Very lightweight
- Use in any environment (Even in prodiction)
Cloud Profiler
- Cloud Profiler
- Low overhead profiler
- gathers
- Major components:
- Profiling agents
- Profiler interface (Vizuliation)
Error Reporting
- How do you identify production problems
- Real time exception montoring
- Aggregate and displays errors reported from cloud services
- Centralize error management
- Error reporting tool can be viewed from desktop
- Aggregates them in to one place
- Uses stack trace
Stack driver/ Cloud monitoring
Stackdriver Service
New service name
Stackdriver Monitoring
Cloud Monitoring
Stackdriver Logging
Cloud Monitoring
Stackdriver Error Reporting
Error Reporting
Stackdriver Trace
Cloud Trace
Stackdriver Profiler
Cloud profiler
Cloud Operations scenarios
Scenario
Solution
Record all operations on a bucket
Turn on data access audit logging
Trace requests accross multiple microservices
Cloud Trace
Identify prominent exceptions or errors for microservices
Error reporting
Debug problem in prodcution
Cloud Debugger
Look at logs for specific requesta
Cloud Logging
Organizing GCP Cloud Resources
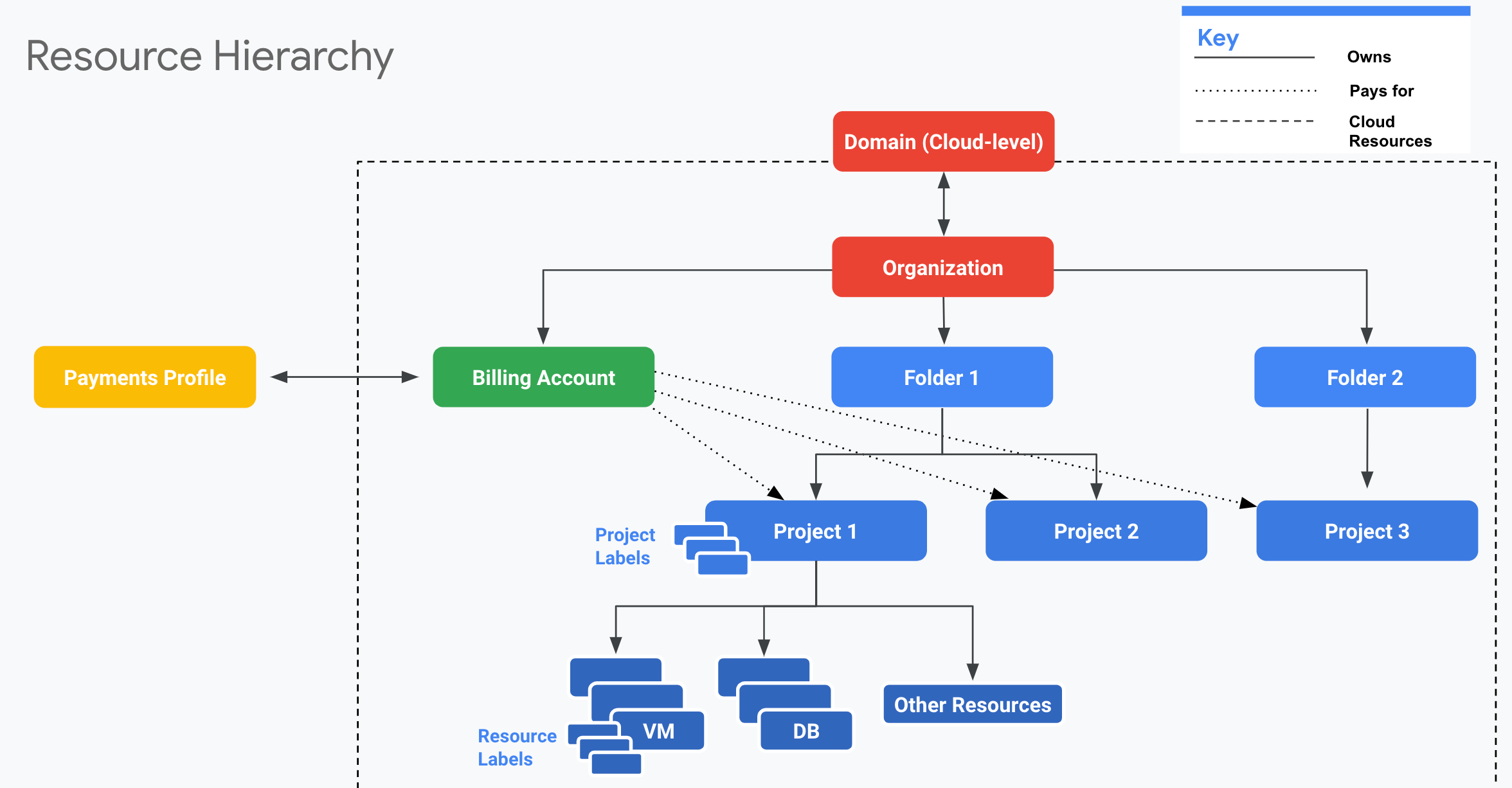
Resource Hierarchy
- Well defined hierarchy
- Organization > Folder > Project > Resources
- Resources are created in Projects
- A folder can contain multiple projects
- An organization can contain multiple folders
Recommendations for Enterprises
- Create separate projects for different environments
- Complete isolation
- Separate folder for each environment
- Isolate environments from one department
- Create a shared folder for shared resources
- One project per application per environment
- App1 and app2
- dev and prod
- Projects:
- A1-DEV
- A1-PROD
- A2-DEV
- A2-PROD
Billing accounts
- Billing account is mandatory
- Every project has one billing account
- You can have multiple billing accounts in one organization
- Create billing accounts representing your organization
- two types of accounts
- Self serve: Billed directly
- Invoiced: Invoice is created and sent to accounts
Managing billing
Budget
- Should set up an alert
- Default threshold is at 50, 90 and 100%
- Can send ti:
- Pub/sub
- Billing data can be exported to:
- Big query
- File export (Now depricated)
Organization Policy Service
- Centralized constraints on all resources
- Configure an organization policy
- Needs organization policy role
- IAM focues on WHO
- Organizatin policy focuses on WHAT
Linux stuff
SSH to VM
- Compute engine uses Key based auth
- two options:
- Metadata managed:
- Manually create and configure individual ssh keys
- OS Login: Manage ssh without managing individual ssh keys
- Your Linux account is automatically linked to your cloud identity
- Go to metadata and set:
- enable-oslogin to true
- Users need to have roles:
- Roled/compute.osLogin
- roles/compute.osAdminLogin
- Windows: Password
- Linux: Keybased
Execute a shutdown script
- Can be used on pre-emptible and non-preemptible VM's
- Runs as:
- Root on linux
- System on windows
- Stored as metadata
- key: shutdown-script
- value: Script
- --metadata-from-file shutdown-script=script.sh from cli
- Can store the scripts in cloud storage
- Run on best effort:
- Not if you do a reset
- Wont run if exceeding grace period
Troubleshoot VM startup
- Are there quota errors?
- Boot disk full?
- Serial port
- Each vm has 4 serial ports
- Serial port output: OS, Bios, Other system level entites
- can access it from cloud console, compute engine api and gcloud cli
- Can send this to cloud logging
- metadata:
- serial-port-logging-enabled = true
- command
- gcloud compute instances get-serial-port-output
- Valid file system
- attach that disk to another vm and see if you can access files
Moving instances between zones and regions
- Can be moved between zones in the same region
- gcloud compute instances move
--zone --destination-zone - Cant move a MIG
- Cant do with local SSD
- Not terminated instances
- Not across regions
- Manual approach
- Snapshot PD's
- create copy of PD's in new region
- Pub/Sub
Pub/Sub
Synchronous communication
- Example:
- Application on your web server make synchronous calls to the logging service
- What if the logging service goes down?
- Solution:
- Create a topic and put the logs on it
- logging service picks them up when it's ready
- Advantages:
- Decouple apps
- Availability: Publisher remains up
- Scalability
- Durability: Message isn't lost if the service is down
Pub/Sub
- Reliable scalable fully managed
- Backbone for HA and scalable solutions
- Autoscales
- Low cost
- Use cases:
- Event ingestion and delivery streaming
- Support push and pull message delivery
How it works
- Publisher - Sender of a message ** Publisher sends a message by making a https request to pubsub.googlepais.com
- Subscriber - Reciever of the message
- Pull
- Subscriber makes the https call
- Push
- Messages are sent to subscribers
- Subscribers provide a web hook endpoint at the time of regestration
- When a message is recieved on the topic, a https post message is sent to the webhooks endpoint
- very flexible:
- Publishers and subscribers, one to many, many to one, many to many
Getting ready with topic and subscriptions
- Topic is created
- Subscribers are created
- Subscribers regisert to the topic
- Each subscriber represents a discrete pull of messages
- Multiple clients pull the same subscriptions
- Multiple clients create a subscription
Sending
- Publisher sends a message
- Message individually delivered to each and every subscription
- Subscribers receive messages
- Push
- Pull
- Subscriber acknowledges
- Messages are removed from subscriptions
- Snapshot:
- Point in time snapshot of that subscription
Best practices
- Use cases:
- Convert synchronous messages to asynchronous
- Useful when consumers cant keep up with producer
- Opensources:
- RabbitMQ
- Apache Kafka
- Apply transformations to IOT stream
- Processing:
- In order
- Exactly one
- option --enable-message-ordering
- Add dataflow in to flow to enable messade dedupe (Exactly once processing)
Dataflow
- Data ETL kinda?
- Streaming batch usaceses
- Real time fraud preventionn
- Sensor data processing
- Log data processing
- Prebuilt templates
Hybrid Cloud
Cloud VPN
- Cloud VPN
- Traffic flows over the internet
- Traffic encrypted using IKE (Internet key exchange)
- 2 types:
- HA VPN
- SLA of 99.99
- 2 external IP's
- BGP
- Classic VPN
- SLA of 99.9
- Static Routing
- Dynamic BGP
- Go for VPN if:
- Low cost
- Lower throughput
- Network to encrypt it
- Just started experimenting with connectivity
HA VPN
- HA VPN
- High Avaliblity
- Regional
- Needs a cloud HA VPN Gateway
- 2 interfaces
Classic VPN
- Classic VPN
- No HA
- Needs a Google compute engine vpn gateway
VPN Gateway - Regional resource
Cloud router enables dynamic routing: Enables automatic route update
Cloud Interconnect
- Cloud interconnect
- High speed
- Low latency
- Not encrypted
- Dedicated interconnect
- High bandwith
- Minimum of 10gbps
- Options are:
- 10gbps
- 100gbps
- 8x10gbps
- 2x100gbps
- Can take 2-3 weeks
- Partner Interconnect
- ideal if you need a lower bandwith connection
- 50mbps to 10gbps
- Data exchanged over private network
- Communicate using VPC network
- Reduces egress costs
- Internet is not used
Hybrid Connectivity
- Hybrid connectivity
- Use different IP ranges
- Backup?
- Cloud interconnect, also establish a VPN
- Direct peering
- You peer to google
- Not a GCP Service
- Not reccomended
- Should use a GCP Service
- BGP routing from the datacentre
Data warehouse
Big query
- Big Query
- Excabyte scale modern data warehouse
- Relational database (SQL Schema, cinsistency)
- Uses SQL like commands
- Organized in to Datasets
- Traditional (Storage + compute) + Modern (Realtime + serverless)
- when talking about data-warehousing:
- Importing and exporting is important
- Variety of formats:
- CSV, Json, Avro, Parquet, OCR, Datastore backup
- Export to GCS (Long term storage)
- Visulize (Data studio)
- Storing long term:
- Compress it
- CSV/ Json
- Avro
- Automatically expire data
- Configurable Table expiratoin
- External sources
- Use external sources in Bigquery:
- Cloud SQL
- BigTable
- Google drive
- Partitinoing
- We are able to partition the table by date, or some value
- When we do a query, only some segments are scanned
- Cluster:
- Group related data
- Example: By category
- Overview:
- Partitioning: Table is divided into segments
- Clustering: Grouping related data by category
- Payment:
- Pay for storage
- Data used in the query
Importing Data in to BigQuery
- Importing in to BQ
- Batch
- Free
- Import after processing by Cloud Dataflow and cloud Dataproc
- Dataproc:
- Managed Hadoop
- Stream
- Expensive
- Pub/sub
- Streaming Inserts
- BQ data transfer service
- Import from External:
- Saas
- S3
- Other Datawarehouses
- Federation
Streaming Data
- Streaming Data
- Not free
- Lots of limitations
- No InsertID
- Can stream up to 1gb per second per project
- InsertID
- Us and EU: 500000 per second
- Per table: 100000
- Maximum bytes per secon: 100
- If streaming millions, use BigTable
Best Practices
- Estimate:
- bq --dry-run
- Cost:
- Expire data
- Load data in Bulk
- Long term storage:
- When not edited for 90 days, cost goes down
- Fast for complex queries
- Not optimized for narrow range queries
- Stream your audit logs from BigQuery to Bigquery
- View in Datastudio
Caching
MemroyStore
- Memory Store
- Fully managed
- Failover patching etc
- HA
- Monitoring setup using cloud monitoring
- Supports Redis and Memcached
- memcached
- Refrence data, database query caching
- Session store
- Redis
- Persistence
- Can be accessed from:
- Most of the compute services
AppEngine Caching
- Appengine caching memcached
- Shared Memcached (free)
- Dedicated:
- Expensive: billed by the GB hour
CDN
- CDN Best practices
- Always cache static content
- Be careful with caching dynamic conent
- Use custom cache keys to improve cache hit ratio
- Any combination of host
- protocal
- host
- query string
- Versioned URL
- setting a version like ?v=1 and then new version is v=2, so you get a cache miss
Devops
CICD
- CICD
- Static code analysis
- Lint, Sonar
- Source code security
- Runtime checks
- Run vulnebility scanner
- Tests
- Unit tests
- Integration tests
- System test
GCP Tools
- Tools
- Cloud Source repositories
- Container Registry
- Build containers
- Jenkins
- Cloud Build
- Spinnaker: Multi-cloud CD
IaC
- Iac
- 2 parts:
- Privision the infra
- Config managment
- Chef, Pupper, ansbile Salt
- Cloud Deployment Manager
- Prevents config drift
- Avoid mistakes
- Put the script in version control
deployment Manager
- Deployment manager
- Template using
- Python
- JinJa2 (Only for simple)
SRE
- SRE
- DevOps++ At google
- SRE team focus on every aspect of an application
- Managed by SLO (Service level objectives)
- Convert business requirments in to measurable items
- Minimize Faffage
- Move fast by reducing cost
- Best practices:
- Handeling excess loads
- Load Shedding
- Reduce it at source
- API LImits
Release Management
- Release managment:
- Goals
- Zero downtime
- Only one version live at a time
- Test with production traffic
- Best practices:
- Small frequent changes
- Automate release managemnt
Recreate
- Recreate
- Install the new version on the new instances
- Most basic approach
- Terminate V1 and roll out V2
- Advantage:
- Cost-effective and fast
- Less compatibility issues
- Disadvantage:
- Rollback is a redeployment
- More downtime
Canary Deployment
- Canary
- Roll out to a subset of instances
- Once metrics are okay
- Roll out to more
- Characheristics
- Fast
- Zero downtime
- No extra infra
- Needs backwards compatibility
A/B Testing
- A/B
- Set up a small new feature and test with half the users
- See if users like somethng
Rolling Approach
- Rolling:
- Roll out the version of the software to 5% at a time (For example)
- Charachterists:
- Slow
- Zero Downtime
- Needs automation
- No needed infrastrucute
- Less impact in a failure
- Rolling with additional batch
- zero reduction in the instances that are running the old version
- you add in another instance whilst it runs
Blue Green Deployment
- Blue-green
- Create a parallel environment with the new version
- Once all tests are done on V1, we switch to the new version
- As far as the end users are concerned, only one release is live
- Characteristics
- Zero downtime
- Easy rollback
- Needs additional Infra
- Zero reduction in ability to serve
- Backwards capacity
- Shadow testing:
- Mirror the traffic to both the versions
- Stubbing needs to be desigend as it may double process a payment (EG)
GKE
Option
Detials
Recreate
Set stratergy > type on deployment to Recreate
Use kubectl set image deploymenr or update deployment yaml yo perform deployment
Rolling Update
Set Stratergy > Type on deploymenr to rolling update
Sue kubectl set image deployment or update deployment yaml to deployment
Blue-green deployment
Create new deployment
Control traffic using Ingress (or service)
Canary deployment
istio mesh
Compliance and regulations
Certifications
- GCP is compliant with several important certificatoins
- ISO
- 27001 (security that helps manage informatino risks
- 27017 (Info and security controls that provision cloud services)
- 27701 Global privacy standard
- PCI DSS Payment card industry data security standards
- SOC 1 - Book keeping
- SOC 2 - Security of provider controls
- COPPA : Childrens online privacy act
- HIPAA : Health insurance for handeling health data
- PHI : Patient health Informatin
- GDPR : Strengthen Data protection in europe
- Customers are responsible for building their applications to that compliance
HIPAA
- HIPAA
- GCP is compliant
- Customers are responsible
- You can execute a Google cloud business associate agreement (BAA)
- Do not use anything not covered by BAA
- Best practices:
- Follow IAM
- Enable Object versioning
- Auditing is exported and to BQ
- Disable caching for PHI
PCI DSS
- PCI DSS
- Enhance cardholder security
- Have separate environment for processing cards
- New account
- Least privelages
- Control inbound
- HTTPS requests from customers
- responses from third party payment processor
- Office network - allowed for auditing
- Strictly control outbount
- HTTPS requests to your payment processor
- GKE and GCE are recommended
- App engine isn't allowing egress firewall rules
- Harden your images
- Only install software that is needed
- Automate as much as you can
- Configuration managment
- Impliment Forseti security
- Opensource tools that improve the security of GCP
- Inventory
- Scanner
- Enforcer
- explain
- Enable VPC flow logs
- Enable transparency logs
- Enable firewall logs
- use google DLP (Data loss prevention) when accessing data
Migration
Planning
- Plan
- Asses the workloads
- Take inventory
- Experiment and make POC
- Caclulate costs
- Chose the workloads to move first
- Plan the foundation
- What type of network
- How to connect
- Security
- Deploy
- Move the data
- gsutil
- transfer appliance
- Deploying:
- Automation
- Automate build and deploy
- IaC
- Optimize the environment
- Ensure that there is logging
- Ensure that managed services are being used
- Optimize costs
Approaches
- Appriaches:
- Lift and Shift
- Replatforming
- Few adjustments to suit the cloud
- Example: Bang it in a container
- Repurchase
- Move to a cloud native porduct
- Refactor
- Serverless compute
- Retire
- EOL
- Retain
- Keep it on premise
Responsibilities
Business requirements
- Business requirments
- Reduce Captial Expenditure
- Just pay OpEx
- Licensing costs
- Computing Costs
- Storage costs
- Network costs
- Personal Costs (people)
- Other costs
- SLA miss
- API
- Reduce csots:
- Managed services
- Autoscaling
- Preepmtible-vms
- Increase innovation
- Devops
- Microservices
- Reduce mean time to recovery
- Improve regulation
Technical Requirments
- technical requirments
- Functional
- Use containers
- Use hardened OS
- Container orchestrations
- Nosql for flexible schema
- Store high volumes at low cost
- Private network (Traffic not over the internet)
- Non-functional aspects
- Avaibility
- Scalability
- Durability
- Security
Planning for HA
- HA
- Geographical distribution
Planning for Scalability
- Scalability
- VM's in a MIG
- Autoscale
- Many regions
- Unmanaged
- No autocaling
- GKE
- Pod and cluster autoscaling for GKE
- Be cautions with resources that cannot scale fast
- Statefull applications are more difficult to scale
- PD:
- Scale Vertically and Horozontally
- Database:
- Pub/sub, BQ Cloud Datastore are serverless
- Bigtable, spanner cloud sql, dataproc are not serverless
Planning for Security
- Secuity
- Confidentiality
- Data is encrypted at rest and transit
- Ensure HTTPS in transit
- Integrity
- Follow IAM best practice
- Role based Access
- Seperation of duties
- Hash verification
- Increases data integrity
- Avalibility
- Firewall
- Auto-failover
- Redundancy
- DDOS
- Anti-spoofing is provided by GCP
- Google frontend
- App engine sits behind google front end
- Firewalling
- Reduce attack surface
- Isolate internal traffic
- Send as much as you can over internal traffic
Cloud Armout
- Cloud Armout
- Prevents against denial of service
- Prevents against:
- OWASP
- xss
- sql injetctions
- Provices security policies
- Use cases:
- Enable access for users with a specific IP address
- Create an allow list
- Block users from an IP
- Create a block list
Digital Signatures
- Digital signatures
- Ensure the integrity of the data received
- nonrepudiation
- Workflow
- Sender performs key operation to create data signature
- Recipient used the public key to verify the digital signature
- Can use CloudKMS
- Provides api and commands to create digital signatures
- Use cases:
- Validating log files
- Validating code builds
Secret Manager
- Secret manager
- Manage how your secret is encrypted
- You can create a Key in KMS
- You can access the key by using the API calling for the password.
Stake holders
- Stakeholder managment
- Execs
- Business owners
- Archi team
- Scrum master
- Dev team
- Testing team
- Sec team
- Compliance team
- Communiation
- Early clear communication
- Identify the stakeholders and communicate
Change Management
- change managment
- People, process and technology (systems)
- Understanding the change and what it means
- Who can make it happen
- Best cycle
- Plan, do check, act
- Do small changes and do multiple iterations
Business continuity planning
- BCP
- How to keep the business running in case of a disaster
- Focuses on IT operations alone
- DR ENV
- Cloud as a DR enviroment
- Backup connection to the cloud
Incident Management
- Incident management
- How best to avoid incidents
- How best to react to it
- Post mortem:
- Not who to blame, but a how to fix
Data Managment
- Data management
- How the data comes in
- Rate it comes in
- What kind of Data?
- How much data
- How long is it stored for
- Life cycle policies